AI-first Earth intelligence platform SkyFi has announced that it has raised $12.7 million in an oversubscribed Series A funding round. The round was co-led by Buoyant Ventures and IronGate Capital Advisors.
This investment will accelerate product development and enhance SkyFi’s technology, including its platform’s user interface and analytical tools. Additionally, the company plans to forge new partnerships with satellite operators to expand its on-demand data offerings and AI-enabled analytic capabilities for leading commercial and government customers worldwide.
Kirk Konert, managing partner at AE Industrial Partners, explains what “Series A” is, and what comes next.
“Series A is; you’ve actually sold your product, now you need the money to actually go make that product or software. Series B is; you’ve taken that next step and have won a significant contract. Now you need help scaling from a prototype to a full manufacturing product. And then Series C; now you have multiple products you need to make. Now you need growth capital.”
SkyFi’s growing network of more than 50 geospatial imagery partners currently provides optical, synthetic aperture radar (SAR), hyperspectral, and aerial imagery, as well as data analytics, to industries including defense, energy, finance, infrastructure and construction, environmental services, agriculture, insurance, and mining.
-0-
Intuitive Machines has completed its acquisition of Lanteris Space Systems (“Lanteris”), formerly Maxar Space Systems. The acquisition, first announced in November 2025, was completed for $800 million before closing adjustments, consisting of $450 million in cash and $350 million in Intuitive Machines Class A common stock.
Lanteris’ Low Earth Orbit, Medium Earth Orbit and geostationary satellites support missile warning and tracking, tactical intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance, Earth observation, and space domain awareness.
The acquisition aligns with the Intuitive Machines vision, strengthening the company’s position as a vertically integrated next generation space prime that is able to build, connect, and operate end-to-end mission solutions unique to the marketplace today.
-0-
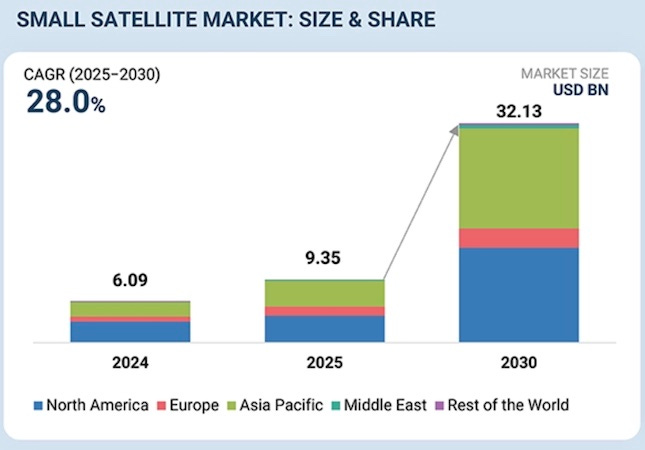
A couple of notable market reports were released this week, both from MarketsandMarkets. The reporting company noted that the Small Satellite Market is projected to grow from $9.35 billion in 2025 to $32.13 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 28.0%. Increased demand for affordable space missions, more frequent launches, and expanded use in communications, Earth observation, and defense applications are all expected to contribute to the upswing.
One major factor is the expansion of LEO constellations for broadband and Earth observation. Increased government use of small satellites for ISR, PNT, and tactical communications is creating steady institutional demand. Additionally, falling manufacturing and launch costs are enabling shorter replacement cycles and more frequent satellite launches. The rising need for high-revisit data in downstream applications is further boosting the adoption of large, scalable small satellite constellations.
The fastest-growing segment in the small satellite market is the commercial sector, as more companies are using satellites for data and revenue-generating services. Commercial satellite operators, telecom firms, and service providers are deploying small satellite constellations to provide broadband connectivity, high-resolution Earth imagery, and continuous monitoring.
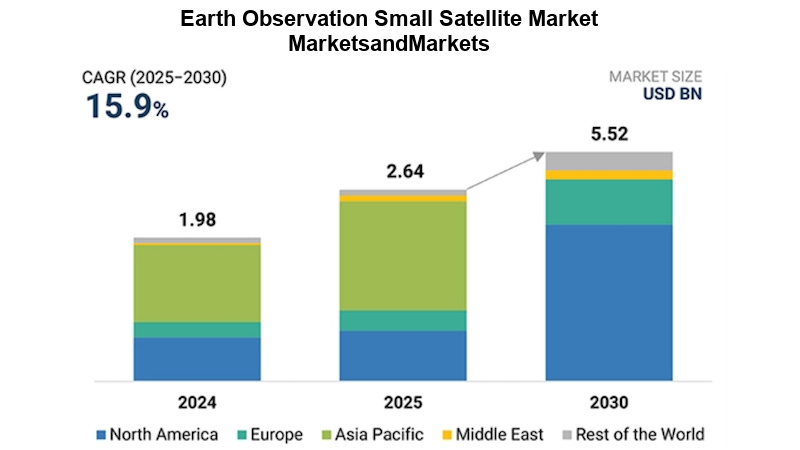
A subset of that market, the Earth Observation Small Satellite Market is projected to grow from $2.64 billion in 2025 to $5.52 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 15.9%. The increasing need for high-frequency Earth observation data drives the EO small satellite market. This data supports planning across defense, environmental management, and commercial analytics.
The 222-2,650 pound mini satellite segment is expected to account for the largest market share in the EO small satellite market during the forecast period. The satellite bus segment is projected to account for the largest market share in the EO small satellite industry during the forecast period. The growth is driven by the increasing demand for modular, reliable, and power-efficient bus platforms.
The FCC has granted a major authorization to Space Exploration Holdings to advance its second-generation Starlink satellite system, marking a significant milestone in global broadband connectivity.
Under this grant, SpaceX is authorized to construct, deploy, and operate an additional 7,500 Gen2 Starlink satellites, bringing the total to 15,000 satellites worldwide. This expansion will enable SpaceX to deliver high-speed, low-latency internet service globally, including enhanced mobile and supplemental coverage from space. The FCC’s decision benefited in particular from the work and collaboration provided by the Commerce Department and NTIA.
The FCC’s decision allows SpaceX to upgrade the Gen2 Starlink satellites with advanced form factors and cutting-edge technology; waive obsolete requirements that prevented overlapping beam coverage and enhanced capacity; add new orbital shells at altitudes ranging from 211 to about 300 miles, optimizing coverage and performance; and provide direct-to-cell connectivity outside the United States and supplemental coverage within the U.S., paving the way for next-generation mobile services.
-0-
Eutelsat, meanwhile, has awarded a contract to Airbus to build an additional 340 OneWeb low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites. Together with the previous batch of 100 satellites procured in December 2024, the total number of satellites ordered is up to 440.
The satellites will be manufactured at Airbus Defense and Space’s Toulouse facility on a newly installed production line, with delivery beginning at the end of 2026.
Eutelsat’s OneWeb low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite network delivers high-speed, low-latency connectivity on a global basis. The availability of these latest satellites will assure full operational continuity for customers of the constellation, progressively replacing early batches coming to end of operational life.
Additionally, they will integrate technology upgrades including advanced digital channelizers, enabling enhanced onboard processing capabilities as well as greater efficiency and flexibility.
-0-
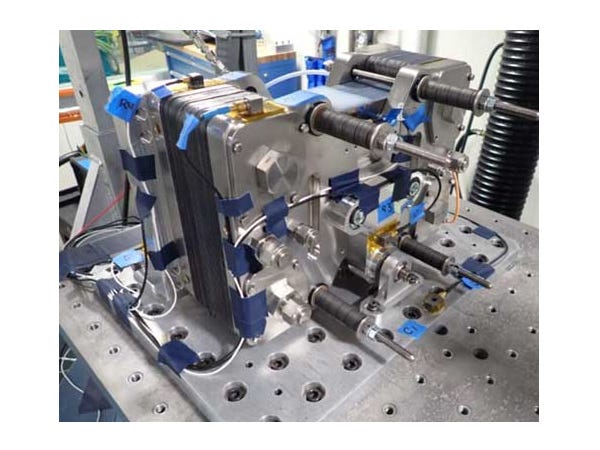
A key milestone for future human spaceflight has been reached with the successful completion of shock and vibration tests on advanced, gravity-independent fuel cell technology developed by Nimbus Power Systems. The tests simulated the anticipated mechanical loads, including launch, for NASA’s upcoming Artemis crewed missions to the Moon. The fuel cell met all performance targets throughout the tests, demonstrating the system’s structural and operational readiness for future flight integration.
Fuel cells react oxygen and hydrogen to produce electricity, heat, and potable water, three vital resources for crewed space operations. Nimbus’ innovative water management technology removes product water via a combination of capillary and hydraulic forces that are uncompromised by the space environment.
Blue Origin currently licenses Nimbus Power System’s fuel cell technology for its Blue Moon Lunar Lander program and other space applications.
-0-
In-Depth this week, CEOs are rewriting the rules of supply chains in an era defined not by efficiency, but by endurance. (Paywall)
Over the last decade, pandemics, geopolitical conflicts, cyber‑attacks, climate disruptions, and inflation have exposed the fragility of global supply systems—built for efficiency, not resilience. The result? Shipping delays, material shortages, and data breaches are now the norm.
Today’s leaders must think like engineers of continuity—not just maintainers of convenience. That means mapping vulnerabilities throughout the network and planning for “five disruptions from now,” not just the next quarter.
Africa is at the center of this shift. With 1.4 billion people and a young workforce, the continent has massive growth potential. But logistics inefficiencies add nearly 40% to the cost of doing business in parts of Africa. The African Continental Free Trade Area—AfCFTA—could boost intra‑continental trade from about 15% to over 50% by 2035, if countries invest in connectivity.
At the heart of this transformation is technology. Artificial intelligence, blockchain, and IoT sensors are now tracking goods with surgical precision. But integration is key—automating outdated processes only speeds up failure.
Sustainability also matters. Supply chains contribute significantly to global carbon emissions, and for African firms, “green logistics” is becoming essential for accessing both climate finance and market opportunities.
A new playbook for executives includes:
Mapping dependencies and failure points;
Digitizing operations with clear goals;
Diversifying sourcing geographically;
Embedding sustainability into performance metrics;
Building agile, culturally aware teams;
Partnering with governments to modernize trade infrastructure.
Supply chains, often called the circulatory system of modern civilization, are now the crucible of corporate leadership. For CEOs, success means not just moving goods, but connecting markets, people, and ideas—fortifying resilience for the next generation of global challenges.
Paid subscribers can read the full analysis on The Journal of Space Commerce under the Supply Chain tab. Other premium articles include a look at export controls and Space Commerce; factors contributing to the costs of small satellites; and how space insurance brokers assess risk.