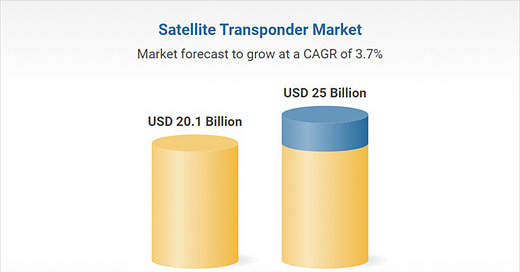
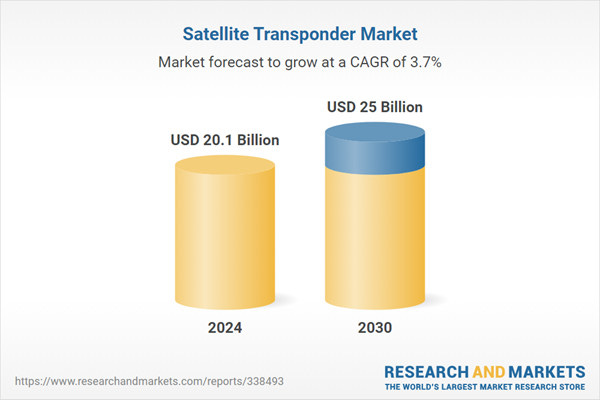
The global market for Satellite Transponder was valued at $20.1 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $25.0 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 3.7% from 2024 to 2030, according to an updated report from Global Industry Analysts.
This report provides an analysis of market trends, drivers, and forecasts to help inform business decisions, and includes the most recent global tariff developments and how they impact the Satellite Transponder market.
Satellite transponders are vital components in the field of satellite communications, acting as the heart of satellite functionality. A transponder receives signals from the Earth, amplifies them, changes their frequency to avoid interference with incoming signals, and then retransmits them back to Earth. This two-way process involves uplink frequencies (Earth to satellite) and downlink frequencies (satellite to Earth), ensuring seamless communication over vast distances. Typically, each satellite houses multiple transponders, each dedicated to a specific bandwidth and service, such as television broadcasting, internet connectivity, and telecommunication services. The importance of transponders lies in their ability to handle high data rates, support various types of data transmission, and maintain the integrity of the signal despite the vast distances it travels.
Technological advancements have significantly enhanced the efficiency and capabilities of satellite transponders. The shift from analog to digital transponders marked a revolutionary change, enabling more data to be transmitted with higher quality and reduced noise. Innovations such as High Throughput Satellites (HTS) and the deployment of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellations have further expanded the potential of satellite transponders. HTS use spot beam technology to provide high data rates and better coverage, making them ideal for internet services and data-intensive applications. Meanwhile, LEO satellites, positioned closer to Earth, reduce latency and improve the speed of data transmission. These advancements have not only improved the performance of transponders but also opened new avenues for their application in various sectors, including disaster management, military communication, and remote sensing.
Despite their critical role, satellite transponders face several challenges that need addressing to maximize their effectiveness. One primary issue is the limited availability of frequency spectrum, which is becoming increasingly congested due to the growing demand for satellite services. This scarcity necessitates efficient spectrum management and the development of technologies that can operate in higher frequency bands, such as the Ka and Ku bands. Another challenge is the susceptibility of satellite signals to interference from both terrestrial and space-based sources.
The growth in the satellite transponder market is driven by several factors directly tied to technological advancements, end-uses, and consumer behavior. Firstly, the increasing demand for high-definition television and the rise of Over-The-Top (OTT) media services require more transponder capacity to deliver high-quality content globally. Secondly, the proliferation of internet usage and the need for broadband connectivity in remote and underserved areas are pushing the demand for satellite-based internet services. This is particularly crucial in regions where terrestrial infrastructure is lacking or infeasible. Thirdly, the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communications necessitates reliable and widespread satellite communication networks. Moreover, the defense and military sectors continue to rely heavily on satellite transponders for secure and resilient communication channels. Lastly, the commercialization of space and the increasing number of private players entering the satellite industry are fostering innovation and reducing costs, further propelling market growth. These factors collectively underscore the dynamic and evolving nature of the satellite transponder market, driving its expansion and adoption across various domains.