Robust Expansion Forecast for the Space Robotics Market
May Reach $14.5 Billion by 2033 According to Verified Market Reports
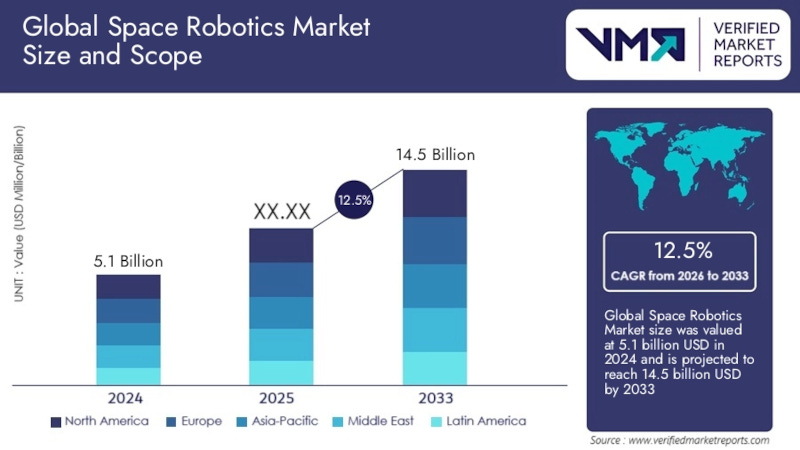
The Space Robotics market is potentially poised for robust expansion, according to a new report from Verified Market Reports. The report indicates that the market, valued at $5.1 billion in 2024 is expected to reach $14.5 billion at a CAGR of 12.5% from 2026 to 2033. Drivers of the projected growth may include accelerating demand for on-orbit servicing, satellite life-extension, debris mitigation and planetary exploration.
Key growth factors encompass technological advancement in autonomy, artificial intelligence, miniaturized sensors, high-precision actuators and modular payload architectures. Investor appetite, strategic partnerships, mergers and acquisitions, increased capital expenditure by OEMs and favorable procurement cycles bolster market penetration and revenue acceleration. Segment analysis highlights commercial satellites, government exploration programs and defense applications as primary end-user verticals.
Space robotics is transitioning from government-led experimentation to commercially scalable deployment. Robotic systems designed for satellite servicing, refueling, inspection, and in-space assembly are becoming integral to cost-optimization strategies for satellite operators. This trend directly supports longer satellite lifecycles, reduced launch frequency, and improved return on space infrastructure investments.
Advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, computer vision, and edge processing are redefining operational capabilities. Autonomous navigation, fault detection, and adaptive manipulation allow space robots to operate with minimal human intervention, mitigating communication latency and enabling deep-space and cislunar missions. These capabilities are increasingly viewed as strategic differentiators.
Space robotics is emerging as a core enabler for defense applications such as satellite inspection, threat monitoring, and orbital asset protection. Governments are prioritizing resilient and responsive space infrastructure, creating sustained demand for robotic platforms that enhance situational awareness and mission assurance.
The rapid growth of small satellites and mega-constellations is driving demand for robotic launch integration, autonomous deployment, and debris mitigation solutions. Space robotics supports scalable constellation management, including precision placement, maintenance, and end-of-life deorbiting.
Robotic systems are foundational to lunar and Martian exploration strategies, enabling surface mobility, regolith handling, construction, and scientific experimentation. These applications reduce human risk while establishing infrastructure for future crewed missions and space-based resource utilization.
Finally, market momentum is strongest in regions where government funding, regulatory clarity, and private-sector innovation are aligned. Strategic partnerships between space agencies, defense organizations, and commercial robotics firms are accelerating technology maturation and market entry.
Autonomy and AI are fundamentally altering the economics of space robotics by reducing reliance on ground-based operations and human-in-the-loop control. Traditional space missions are constrained by communication delays, limited bandwidth, and high operational staffing costs. Intelligent robotic systems equipped with autonomous decision-making, adaptive control, and predictive maintenance capabilities can execute complex tasks independently, significantly lowering mission operating expenses.
Despite strong momentum, the space robotics market faces several restraints, including high upfront development costs, technical complexity, regulatory uncertainty, and mission risk. Space-qualified robotic systems must withstand extreme environments, radiation exposure, and long-duration missions, driving up research, testing, and certification expenses.
Industry participants are mitigating these challenges through modular design architectures, digital twins, and simulation-driven development to reduce testing cycles and failure rates. Public-private partnerships are also playing a critical role by sharing financial risk and accelerating validation through government-sponsored missions. Additionally, clearer regulatory frameworks around on-orbit servicing and debris mitigation are reducing legal uncertainty, enabling faster commercialization.