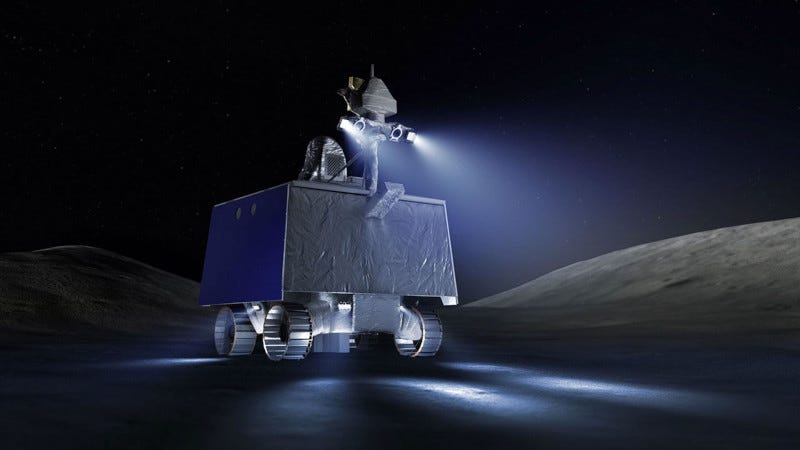
Are you interested in a Moon Rover ... low miles, never used? After the program was cancelled in 2024, NASA is now looking to secure a public/private partnership and land and operate NASA’s VIPER (Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover) mission on the Moon.
As part of an agreement, NASA would contribute the existing VIPER rover as-is. Potential partners would need to arrange for the integration and successful landing of the rover on the Moon, conduct a science/exploration campaign, and disseminate VIPER-generated science data. The partner may not disassemble the rover and use its instruments or parts separately from the VIPER mission. NASA’s selection approach will favor proposals that enable data from the mission’s science instruments to be shared openly with anyone who wishes to use it.
This new announcement comes after NASA issued a Request for Information on Aug. 9, 2024, to seek interest from American companies and institutions in conducting a mission using the agency’s VIPER Moon rover after the program was canceled in July 2024. Any partnership would work under a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement. This type of partnership allows both NASA and an industry partner to contribute services, technology, and hardware to the collaboration.
The Announcement for Partnership Proposal contains proposal instructions and evaluation criteria for a new Lunar Volatiles Science Partnership. Responses are due Thursday, Feb. 20. After evaluating submissions, any selections by the agency will require respondents to submit a second, more detailed, proposal. NASA is expected to make a decision on the VIPER mission this summer.
-0-
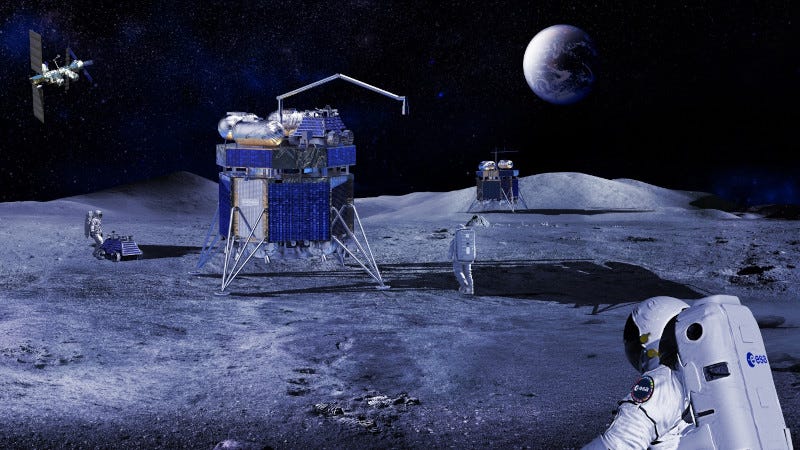
While we're on the subject of lunar exploration, ESA has awarded a contract valued at some $886 million to Thales Alenia Space related to the design, the development and the delivery of the Lunar Descent Element (LDE) for ESA’s Argonaut Mission, including responsibility for mission design and integration.
Planned to be launched from the 2030s, Argonaut will deliver cargo, infrastructure and scientific instruments to the Moon’s surface.
The first mission is envisioned to deal with delivery of dedicated navigation and telecommunication payloads as well as an energy generation and storage system, as European enterprises to explore the Lunar southern area.
The Argonaut spacecraft consists of three main elements: the lunar descent element (LDE) for flying to the Moon and landing on the target, the cargo platform one, which is the interface between the lander and its payload, and finally, the element that the mission designers want to send to the Moon.
-0-
Meanwhile, a joint request for research proposals to study and advance long-term human habitation and exploration in space has been issued by Vast and SpaceX.
Building on their established partnership, the two companies seek high-impact research projects to support humanity on Earth and advance our capacity to live and work in Earth orbit and beyond. Submitted proposals will be evaluated based on scientific and technical merit, feasibility, and alignment with mission objectives. Approved research proposals will be able to leverage the capabilities of the Haven-1 Lab, Dragon spacecraft, and/or private astronaut missions to the International Space Station (ISS).
Haven-1 is scheduled to be the world’s first commercial space station and crewed microgravity research, development, and manufacturing platform. This groundbreaking facility will enable cutting-edge research and technological advancements, opening new frontiers in space science.
While no direct funding will be provided to the research project, Vast and SpaceX will offer selected researchers access to a hosted orbital laboratory, on-orbit crew time, and support for project design and flight qualification—at no cost.
-0-
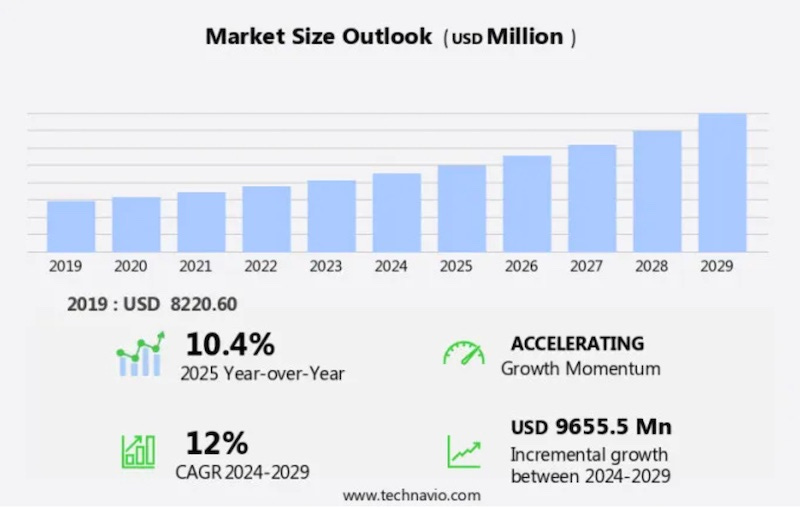
It's no secret that Earth observation is one of the cornerstones of the new space economy, and the appetite for EO data seems to continue to grow. According to a new report from Technavio, The satellite-based earth observation market size is estimated to increase by $9.65 billion at a CAGR of 12% between 2024 and 2029.
North America is estimated to contribute 43%. To the growth of the global market. The Satellite-Based Earth Observation Market report forecasts market growth by revenue at global, regional & country levels from 2017 to 2027. The United States dominates the global satellite-based Earth Observation (EO) market, owning approximately one-third of the current Earth-orbiting satellites. Since the industry's inception, the US has been a pioneer, utilizing satellites for communications, surveillance and intelligence, national security, weather forecasting, disaster management, environmental monitoring, and navigation. NASA spearheads most US satellite-based EO missions. However, in the last decade, numerous private companies have emerged, offering satellite imagery analysis and Value-Added Services (VAS). Some of these enterprises also manufacture and launch their small satellites for data collection.
The defense segment held a substantial share in the global satellite-based Earth observation market in 2023 due to increasing defense spending on satellite technologies for surveillance, security, and intelligence purposes by emerging nations like China, India, and Russia.
Market growth is driven by the need for natural catastrophe prevention, climate change mitigation, and scientific research and development. However, market restraints include highly trained workers, encrypted data security, big data management, launch costs, and satellite production.
-0-
Another prominent player in the new space economy is satellite communications, and that market is also poised for some significant growth, according to a new report from the Business Research Company.
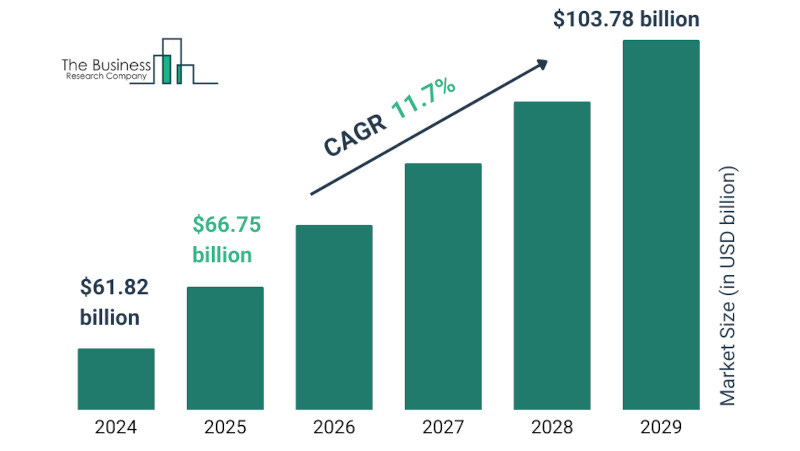
The Satellite Communication market value stood at $61.82 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $66.75 billion in 2025 with a CAGR of 8.0 percent. And the company projects that the future looks bright for the market, with its size expected to shoot up to $103.78 billion in 2029 at an impressive CAGR of 11.7 percent.
The market appears to be largely driven by the increasing adoption of low-earth orbit satellites across sectors. The technology is revolutionizing internet and digital communication, bolstering market growth. Robust government support is driving the growth of the satellite communication market in the forecast period. Government investment will support research and development activities, new technology developments and projects.
North America led the Satellite Communication market in 2024. However, it is Asia-Pacific that's expected to demonstrate the fastest growth in the forecast period.
-0-
This programming note, in the coming months, you’ll notice more articles and podcasts that are behind a paywall. Paid subscribers will have first access to that content, but it will eventually be made available to all subscribers. But to be among the first to see them, please consider upgrading to a paid subscription to The Journal of Space Commerce. And thank you in advance.
You might also like: