LEO Satellite Market worth $23.2 Billion by 2029
Driven by the Growing Need for Earth Observation Imagery and Analytics
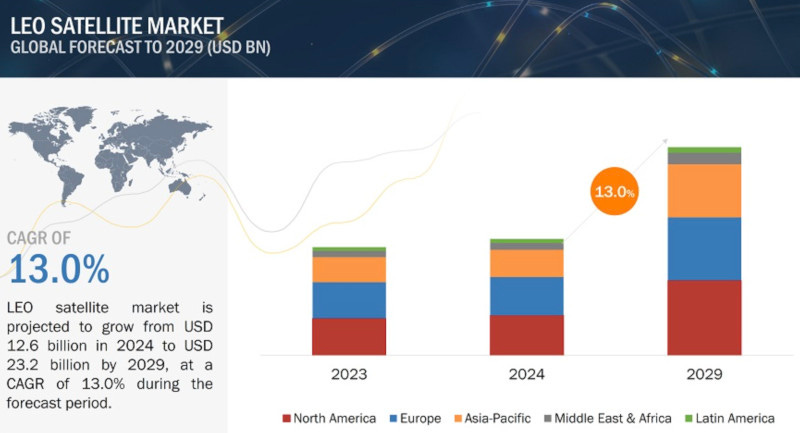
The LEO satellite market is projected to grow from $12.6 billion in 2024 to $23.2 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 13.0% from 2024 to 2029 according to a new report by MarketsandMarkets. The market growth can be attributed to the growing need for earth observation imagery and analytics.
The LEO satellite market holds a huge potential for data service provid…