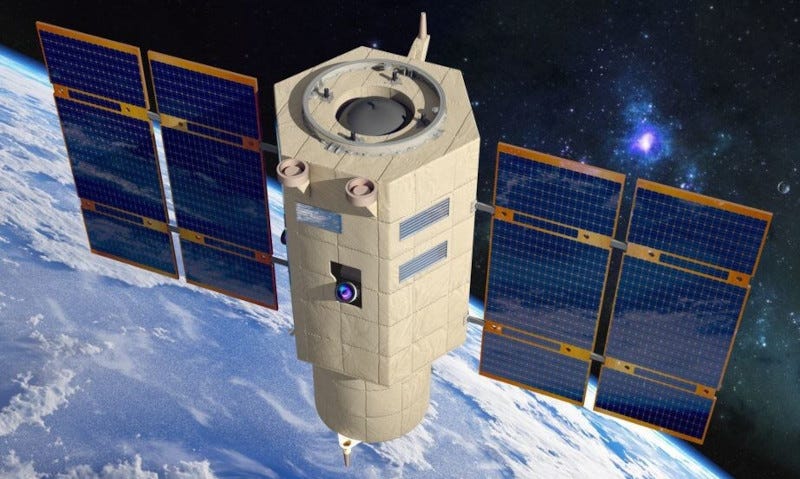
JUPITER Camera Successfully Launched Aboard NAOS Satellite
Supports a Wide Span of Earth Observation Missions
The Elbit Systems advanced JUPITER space camera launched Tuesday aboard the National Advanced Optical System (NAOS) satellite, supporting a wide span of earth Observation missions, including military operations, environmental monitoring and scientific research. The NAOS satellite, manufactured by OHB Italia S.p.A., was launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
Developed by Elbit Systems ISTAR&EW - ELOP, JUPITER is one of the world's most advanced space cameras, featuring a very large aperture and an exceptionally lightweight design.
The camera is multispectral, offering a combination of imaging channels:
A high-resolution panchromatic channel (black and white), which captures fine spatial details across the full visible spectrum.
RGB channels (red, green, blue) for true-color imaging.
A NIR channel (Near-Infrared), which enables analysis of vegetation health, water content, and material properties.
These channels are provided at an exceptional resolution ratio, ideal for advanced image fusion and analysis. JUPITER is capable of capturing continuous long image strips with a swath, allowing efficient coverage of large geographic areas in a single orbital overpass.
The data generated by the JUPITER camera is designed for seamless integration with both onboard systems and ground station analytics platforms. Its compatibility with advanced image processing and AI engines enables the extraction of actionable insights, supporting informed decision-making across a wide range of applications.
In addition to the camera, Elbit Systems developed and supplied advanced algorithms to support the ground segment of the NAOS mission, enhancing image analysis capabilities.
This achievement is the result of a close collaboration between OHB Italia and Elbit Systems, combining satellite engineering excellence with top-tier imaging technology to deliver one of the highest-performing spaceborne optical systems in the world.



