CubeSat Will Facilitate Lunar Calibration Efforts
Blue Canyon Technologies Supports ARCSTONE Mission
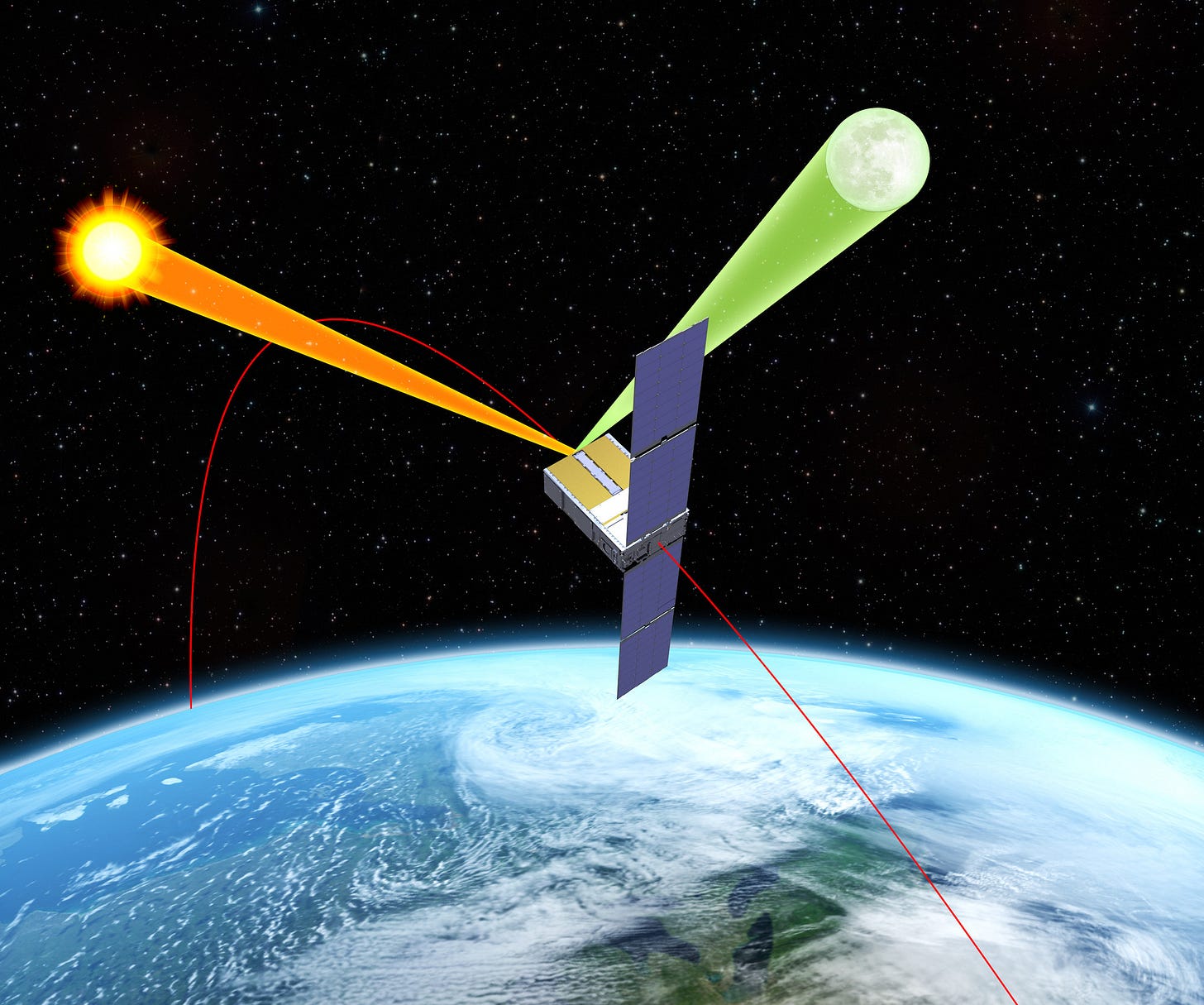
A CubeSat supporting ARCSTONE, a NASA mission to measure lunar spectral reflectance, has been launched by Blue Canyon Technologies. Lunar spectral reflectance is the way sunlight is reflected back from the Moon's surface at different wavelengths of light. The ARCSTONE mission will use the data it collects to help calibrate space-based imagers for earth observation.
"The Moon is an excellent and available source for calibration with the potential for high accuracy."
Dr. Constantine Lukashin, NASA
Sunlight, reflected from Earth, carries a vast amount of information into space about the planet's surface, atmosphere and its composition. ARCSTONE will use a spectrometer – a scientific instrument that measures and analyzes light by separating it into spectrums – to precisely measure reflected sunlight from the entire lunar disk. This cannot be done as effectively from Earth’s surface due to interference from the atmosphere.
“One of the most challenging tasks in remote sensing from space is achieving required instrument calibration accuracy on-orbit,” said Dr. Constantine Lukashin, physical research scientist at NASA’s Langley Research Center and principal investigator for the ARCSTONE mission. “The Moon is an excellent and available source for calibration with the potential for high accuracy. ARCSTONE will enable multiple spaceborne assets to improve quality of measurements and data products for generations to come.”
“Blue Canyon’s advanced spacecraft technology will support ARCSTONE in its efforts to enable high-accuracy lunar calibration standards for past, present, and future sensors in low-Earth and geostationary orbits,” said Chris Winslett, general manager of Blue Canyon Technologies.
In addition to building the spacecraft, Blue Canyon Technologies will also provide mission operations support, making approximately three contacts with the satellite per day.
The ARCSTONE spacecraft is Blue Canyon’s 66th CubeSat to launch into orbit, bringing the company’s total number of CubeSat and microsatellite spacecraft launched to 84 units. The satellite was designed using the company’s guidance, navigation and control systems to enable high pointing accuracy and agility for targeting. Pointing accuracy describes the process of orienting a spacecraft which is especially important in data collection missions. The spacecraft was assembled at Blue Canyon’s CubeSat factory in Boulder, Colo., and mission operations will be conducted from the company’s Mission Operations Center in Lafayette.