AstroVision, Lunar Optical Navigation, Demonstrated at Space Symposium
Space-ng Technology Flew on the Blue Ghost Lunar Mission
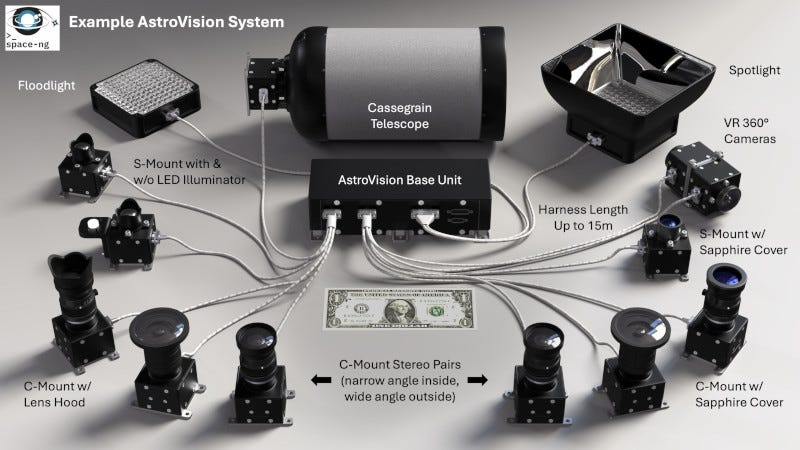
Technology that contributed to the success of the Aerospace's Blue Ghost Mission 1 (BGM1) landing at Mare Crisium has been on display at Space Symposium this week. Space-ng optical navigation software provided terrain relative navigation, hazard detection, and attitude determination from lunar orbit to the surface.
"Optical navigation is critical in situ…